

"Hunefer's Book of the Dead, detail with Horus and pavilion" by Steven Zucker is licensed under CC BY 2.0
Ancient Egypt, civilization in northeastern Africa that dates from the 4th millennium bc. Its many achievements, preserved in its art and monuments, hold a fascination that continues to grow as archaeological finds expose its secrets. This article focuses on Egypt from its prehistory through its unification under Menes (Narmer) in the 3rd millennium bc—sometimes used as a reference point for Egypt’s origin—and up to the Islamic conquest in the 7th century ad. More...
SOURCE: "Ancient Egypt." Britannica Academic, Encyclopædia Britannica, 23 May. 2013.
Egyptology, the study of pharaonic Egypt, spanning the period c. 4500 bce to ce 641. Egyptology began when the scholars accompanying Napoleon Bonaparte’s invasion of Egypt (1798–1801) published Description de l’Égypte (1809–28), which made large quantities of source material about ancient Egypt available to Europeans. More...
SOURCE: "Egyptology." Britannica Academic, Encyclopædia Britannica, 23 May. 2013.

"Great Sphinx of Giza" by Jack Versloot is licensed under CC BY 2.0
Egyptian art and architecture, the ancient architectural monuments, sculptures, paintings, and decorative crafts produced mainly during the dynastic periods of the first three millennia bce in the Nile valley regions of Egypt and Nubia. The course of art in Egypt paralleled to a large extent the country’s political history, but it depended as well on the entrenched belief in the permanence of the natural, divinely ordained order. More...
SOURCE: "Egyptian art and architecture." Britannica Academic, Encyclopædia Britannica, 1 Jun. 2016.
History of Mesopotamia, history of the region in southwestern Asia where the world’s earliest civilization developed. The name comes from a Greek word meaning “between rivers,” referring to the land between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, but the region can be broadly defined to include the area that is now eastern Syria, southeastern Turkey, and most of Iraq. The region was the centre of a culture whose influence extended throughout the Middle East and as far as the Indus valley, Egypt, and the Mediterranean. This article covers the history of Mesopotamia from the prehistoric period up to the Arab conquest in the 7th century ce. More...
SOURCE: "History of Mesopotamia." Britannica Academic, Encyclopædia Britannica, 15 Apr. 2016.
Click on Image for Full-Size Version of Timeline.
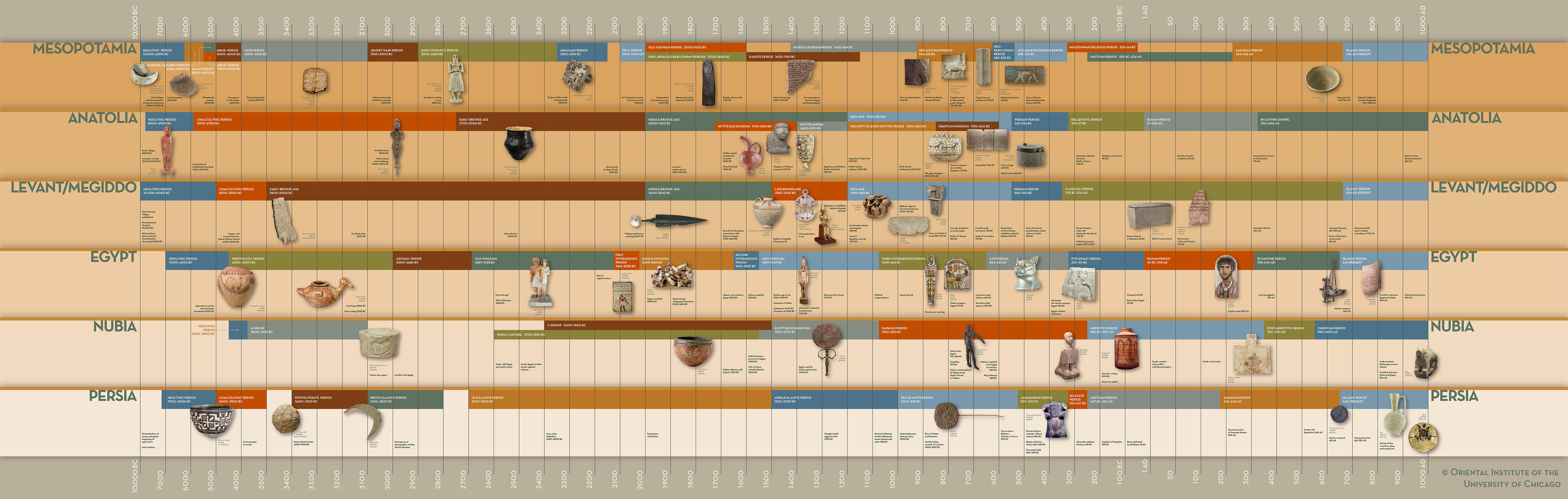
Credit: "Courtesy of the Oriental Institute of the University of Chicago"

"Winged Bull from Khorsabad" by Library & Archives @ Royal Ontario Museum is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 2.0
Mesopotamian art and architecture, the art and architecture of the ancient Mesopotamian civilizations. The name Mesopotamia has been used with varying connotations by ancient writers. If, for convenience, it is to be considered synonymous with the modern state of Iraq, it can be seen in terms of two fairly well-defined provinces: a flat alluvial plain in the south and, in the north, the uplands through which the country’s twin rivers flow in their middle courses. More...
SOURCE: "Mesopotamian art and architecture." Britannica Academic, Encyclopædia Britannica, 8 Oct. 2010.

Ancient Middle East, history of the region from prehistoric times to the rise of civilizations in Mesopotamia, Egypt, and other areas. More...

Syro-Palestinian art and architecture, the art and architecture of ancient Syria and Palestine. The countries bordering the Mediterranean between the Sinai Peninsula and the Nur Dağları (Amanus Mountains), to which the names Palestine and Syria are often loosely applied, had in fact no geographic integrity or clear historical definition. The interior of Syria and its extension beyond the Euphrates have in the past always been separated ethnographically, and sometimes politically, from the coastal cities of the Levant, the associations of which were with Cilicia and the trade routes of Palestine. In early historical times both Syria and Palestine, however, were continuously dominated by one or other of the great imperial powers—Egyptian, Mesopotamian, or Hittite. More...
SOURCE: "Syro-Palestinian art and architecture." Britannica Academic, Encyclopædia Britannica, 2 Aug. 2002.
