Your essay should be typed and double-spaced on standard-sized paper (8.5" x 11"), with 1" margins on all sides. You should use a font consistently throughout the paper. APA recommends using either a sans serif font such as 11-point Calibri, 11-point Arial, or 10-point Lucida Sans Unicode, or a serif font such as 12-point Times New Roman, 11-point Georgia, or 10-point Computer Modern.
Include a page header (also known as the “running head”) at the top of every page. For a student paper, this only includes the page number. To create a page header/running head, insert page numbers flush right.
Your essay should include four major sections: the Title Page, Abstract, Main Body, and References.
Note: APA 7 provides slightly different directions for formatting the title pages of professional papers (e.g., those intended for scholarly publication) and student papers (e.g., those turned in for credit in a high school or college course).
The title page should contain the title of the paper, the author's name, and the institutional affiliation. A student paper should also include the course number and name, instructor name, and assignment due date. Include the page header (described above) flush left with the page number flush right at the top of the page.
Type your title in upper and lowercase letters centered in the upper half of the page. The title should be centered and written in boldface. APA recommends that your title be focused and succinct and that it should not contain abbreviations or words that serve no purpose. Your title may take up one or two lines. All text on the title page, and throughout your paper, should be double-spaced.
Beneath the title, type the author's name: first name, middle initial(s), and last name. Do not use titles (Dr.) or degrees (PhD).
Beneath the author's name, type the institutional affiliation, which should indicate the location where the author(s) conducted the research.
Student APA title page

Example of a student title page in APA 7 format
APA Style uses a unique headings system to separate and classify paper sections. Headings are used to help guide the reader through a document. The levels are organized by levels of subordination, and each section of the paper should start with the highest level of heading. There are 5 heading levels in APA. Regardless of the number of levels, always use the headings in order, beginning with level 1. The format of each level is illustrated below:
|
APA Headings |
|
|
Level |
Format |
|
1 |
Centered, Boldface, Title Case Heading Text starts a new paragraph. |
|
2 |
Flush left, Boldface, Title Case Heading Text starts a new paragraph. |
|
3 |
Flush Left, Boldface Italic, Title Case Heading Text starts a new paragraph. |
|
4 |
Indented, Boldface Title Case Heading Ending With a Period. Paragraph text continues on the same line as the same paragraph. |
|
5 |
Indented, Boldface Italic, Title Case Heading Ending With a Period. Paragraph text continues on the same line as the same paragraph. |
Thus, if the article has four sections, some of which have subsections and some of which don’t, use headings depending on the level of subordination. Section headings receive level one format. Subsections receive level two format. Subsections of subsections receive level three format. For example:
Method (Level 1)
Site of Study (Level 2)
Participant Population (Level 2)
Teachers (Level 3)
Students (Level 3)
Results (Level 1)
Spatial Ability (Level 2)
Test One (Level 3)
Teachers With Experience. (Level 4)
Teachers in Training. (Level 4)
Teaching Assistants. (Level 5)
Test Two (Level 3)
Kinesthetic Ability (Level 2)
In APA Style, the Introduction section never gets a heading and headings are not indicated by letters or numbers. For subsections in the beginning of a paper (introduction section), the first level of subsection will use Level 2 headings — the title of the paper counts as the Level 1 heading. Levels of headings will depend upon the length and organization of your paper. Regardless, always begin with level one headings and proceed to level two, etc.
Special headings called section labels are used for certain sections of a paper which always start on a new page.
These labels should be positioned on their own line at the top of the page where the section starts, in bold and centered.
APA also allows for seriation in the body text to help authors organize and present key ideas. For lists where a specific order or numbered procedure is necessary, use an Arabic numeral directly followed by a period, such as:
On the basis of four generations of usability testing on the Purdue OWL, the Purdue OWL Usability Team recommended the following:
Numbered lists should contain full sentences or paragraphs rather than phrases. The first word after each number should be capitalized, as well as the first word in any following sentence; each sentence should end with a period or other punctuation.
For lists that do not communicate hierarchical order or chronology, use bullets:
In general, participants found the user-centered OWL mock up to be easier to use. What follows are samples of participants' responses:
Authors may also use seriation for paragraph length text.
For seriation within sentences, authors may use letters:
On the basis of research conducted by the usability team, OWL staff have completed (a) the OWL site map; (b) integrating graphics with text on the OWL homepage; (c) search boxes on all OWL pages except the orange OWL resources (that is pending; we do have a search page); (d) moving the navigation bar to the left side of pages on all OWL resources except in the orange area (that is pending); (e) piloting the first phase of the three-tiered navigation system, as illustrated in the new Engagement section.
Authors may also separate points with bullet lists:
On the basis of the research conducted by the usability team, OWL staff have completed
If your bulleted list is part of the sentence and is not preceded by a colon, treat the bullets like a part of the sentence, adhering to standard capitalization and punctuation. This option is helpful for complex or longer bulleted sentences that may be more difficult to read without the aid of punctuation. For items in a bulleted list that are phrases rather than sentences, no punctuation is necessary.
Source:
American Psychological Association. (n.d.). Sample Papers. https://apastyle.apa.org/style-grammar-guidelines/paper-format/sample-papers
Purdue Online Writing Lab. (n.d.). APA Headings and Seriation. Purdue Online Writing Lab. https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/apa_style/apa_formatting_and_style_guide/apa_headings_and_seriation.html
*Note: these guidelines are specifically for STUDENT papers. For Professional papers (those being submitted for scholarly publication), additional instructions apply - please consult https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/apa_style/apa_formatting_and_style_guide/general_format.html
The purpose of tables (any graphic that uses a row and column structure to organize information) and figures (any illustration or image other than a table) in documents is to enhance your readers' understanding of the information in the document; usually, large amounts of information can be communicated more efficiently in tables or figures. However, visuals must be used to assist communication, not to use up space, or disguise marginally significant results behind a screen of complicated statistics. Ask yourself if the table or figure is necessary. For example, it is better to present simple descriptive statistics in the text, not in a table.
Because tables and figures supplement the text, refer in the text to all tables and figures used and explain what the reader should look for when using the table or figure. Focus only on the important point the reader should draw from them, and leave the details for the reader to examine on their own.
If you are using figures, tables and/or data from other sources, be sure to gather all the information you will need to properly document your sources.
Each table and figure must be intelligible without reference to the text, so be sure to include an explanation of every abbreviation (except the standard statistical symbols and abbreviations).
Number all tables sequentially as you refer to them in the text (Table 1, Table 2, etc.), likewise for figures (Figure 1, Figure 2, etc.). Abbreviations, terminology, and probability level values must be consistent across tables and figures in the same article. Likewise, formats, titles, and headings must be consistent. Do not repeat the same data in different tables.
Data in a table that would require only two or fewer columns and rows should be presented in the text. More complex data is better presented in tabular format. In order for quantitative data to be presented clearly and efficiently, it must be arranged logically, e.g. data to be compared must be presented next to one another (before/after, young/old, male/female, etc.), and statistical information (means, standard deviations, N values) must be presented in separate parts of the table. If possible, use canonical forms (such as ANOVA, regression, or correlation) to communicate your data effectively.
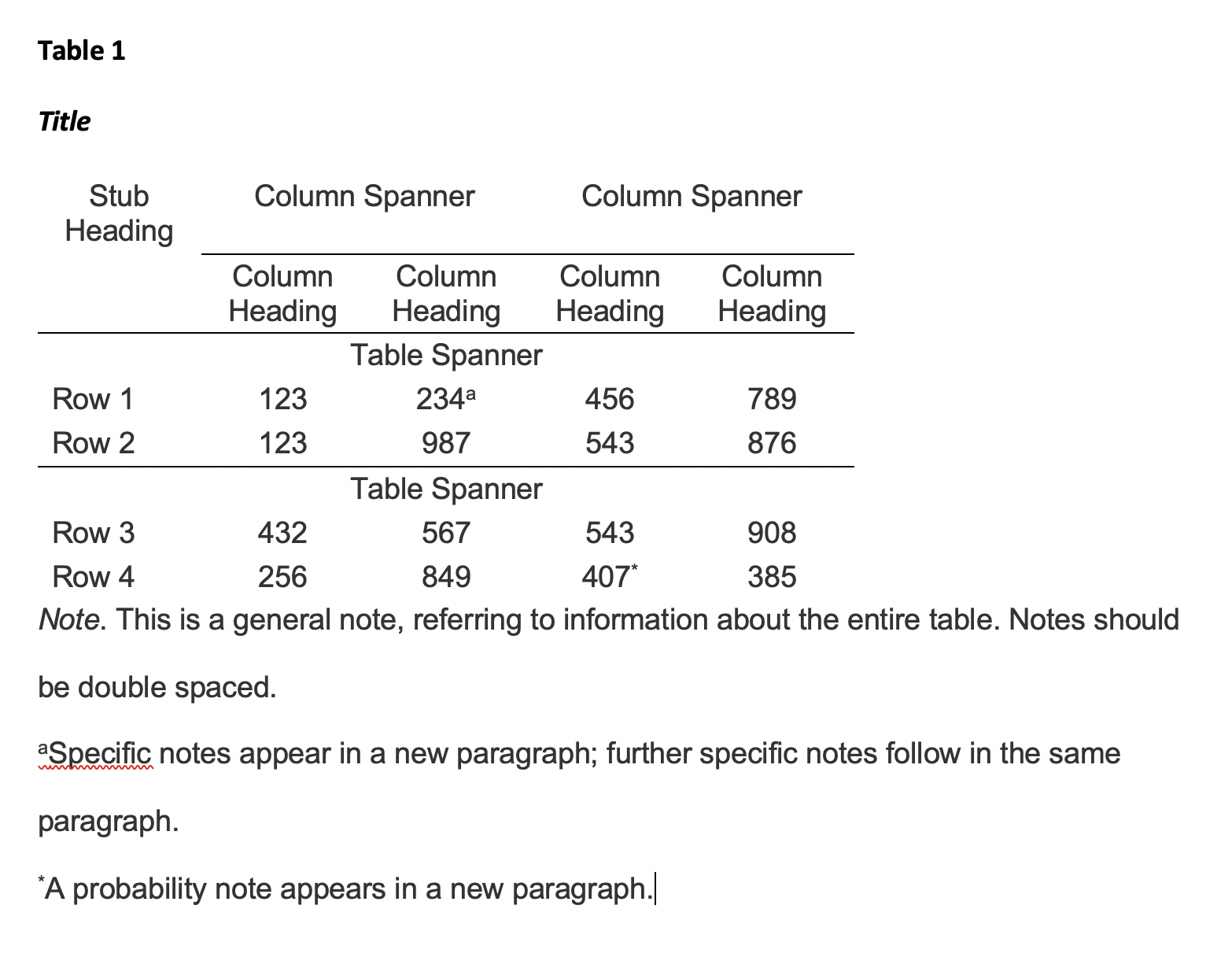
A generic example of a table with multiple notes formatted in APA 7 style.
Number all tables with Arabic numerals sequentially. Do not use suffix letters (e.g. Table 3a, 3b, 3c); instead, combine the related tables. If the manuscript includes an appendix with tables, identify them with capital letters and Arabic numerals (e.g. Table A1, Table B2).
Like the title of the paper itself, each table must have a clear and concise title. Titles should be written in italicized title case below the table number, with a blank line between the number and the title. When appropriate, you may use the title to explain an abbreviation parenthetically.
Comparison of Median Income of Adopted Children (AC) v. Foster Children (FC)
Keep headings clear and brief. The heading should not be much wider than the widest entry in the column. Use of standard abbreviations can aid in achieving that goal. There are several types of headings:
All columns must have headings, written in sentence case and using singular language (Item rather than Items) unless referring to a group (Men, Women). Each column’s items should be parallel (i.e., every item in a column labeled “%” should be a percentage and does not require the % symbol, since it’s already indicated in the heading). Subsections within the stub column can be shown by indenting headings rather than creating new columns:
Chemical Bonds
Ionic
Covalent
Metallic
The body is the main part of the table, which includes all the reported information organized in cells (intersections of rows and columns). Entries should be centred unless left aligning them would make them easier to read (longer entries, usually). Word entries in the body should use sentence case. Leave cells blank if the element is not applicable or if data were not obtained; use a dash in cells and a general note if it is necessary to explain why cells are blank. In reporting the data, consistency is key: Numerals should be expressed to a consistent number of decimal places that is determined by the precision of measurement. Never change the unit of measurement or the number of decimal places in the same column.
There are three types of notes for tables: general, specific, and probability notes. All of them must be placed below the table in that order.
General notes explain, qualify or provide information about the table as a whole. Put explanations of abbreviations, symbols, etc. here.
Example: Note. The racial categories used by the US Census (African-American, Asian American, Latinos/-as, Native-American, and Pacific Islander) have been collapsed into the category “non-White.” E = excludes respondents who self-identified as “White” and at least one other “non-White” race.
Specific notes explain, qualify or provide information about a particular column, row, or individual entry. To indicate specific notes, use superscript lowercase letters (e.g. a, b, c), and order the superscripts from left to right, top to bottom. Each table’s first footnote must be the superscript a.
a n = 823. b One participant in this group was diagnosed with schizophrenia during the survey.
Probability notes provide the reader with the results of the tests for statistical significance. Asterisks indicate the values for which the null hypothesis is rejected, with the probability (p value) specified in the probability note. Such notes are required only when relevant to the data in the table. Consistently use the same number of asterisks for a given alpha level throughout your paper.
*p < .05. **p < .01. ***p < .001
If you need to distinguish between two-tailed and one-tailed tests in the same table, use asterisks for two-tailed p values and an alternate symbol (such as daggers) for one-tailed p values.
*p < .05, two-tailed. **p < .01, two-tailed. †p <.05, one-tailed. ††p < .01, one-tailed.
Tables should only include borders and lines that are needed for clarity (i.e., between elements of a decked head, above column spanners, separating total rows, etc.). Do not use vertical borders, and do not use borders around each cell. Spacing and strict alignment is typically enough to clarify relationships between elements.
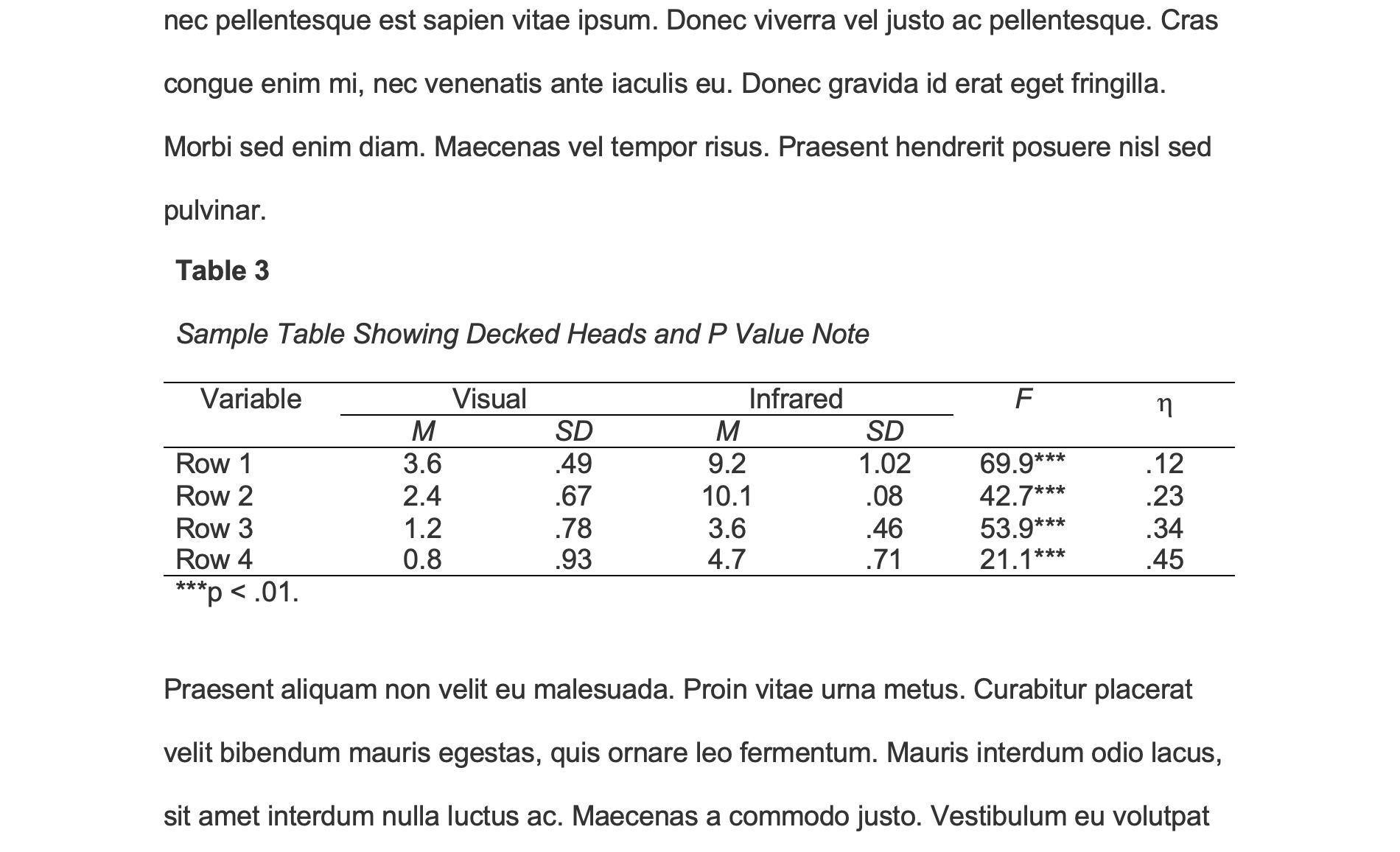
Example of a table in the text of an APA 7 paper. Note the lack of vertical borders.
If using tables from an external source, copy the structure of the original exactly, and cite the source in accordance with APA style.
(Taken from the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association, 7th ed., Section 7.20)
Figures include all graphical displays of information that are not tables. Common types include graphs, charts, drawings, maps, plots, and photos. Just like tables, figures should supplement the text and should be both understandable on their own and referenced fully in the text.
In preparing figures, communication and readability must be the ultimate criteria. Simplicity is key; special effects and poor design can distract from and distort the data, and make the reader doubt your credibility.
All figures that are part of the main text require a number using Arabic numerals (Figure 1, Figure 2, etc.). Numbers are assigned based on the order in which figures appear in the text and are bolded and left aligned.
Under the number, write the title of the figure in italicized title case. The title should be brief, clear, and explanatory, and both the title and number should be double spaced.
The image of the figure is the body, and it is positioned underneath the number and title. The image should be legible in both size and resolution; fonts should be sans serif, consistently sized, and between 8-14 pt. Title case should be used for axis labels and other headings; descriptions within figures should be in sentence case. Shading and colour should be limited for clarity; use patterns along with colour and check contrast between colours with free online checkers to ensure all users (people with colour vision deficiencies or readers printing in grayscale, for instance) can access the content. Gridlines and 3-D effects should be avoided unless they are necessary for clarity or essential content information.
Legends, or keys, explain symbols, styles, patterns, shading, or colours in the image. Words in the legend should be in title case; legends should go within or underneath the image rather than to the side. Not all figures will require a legend.
Notes clarify the content of the figure; like tables, notes can be general, specific, or probability. General notes explain units of measurement, symbols, and abbreviations, or provide citation information. Specific notes identify specific elements using superscripts; probability notes explain statistical significance of certain values.
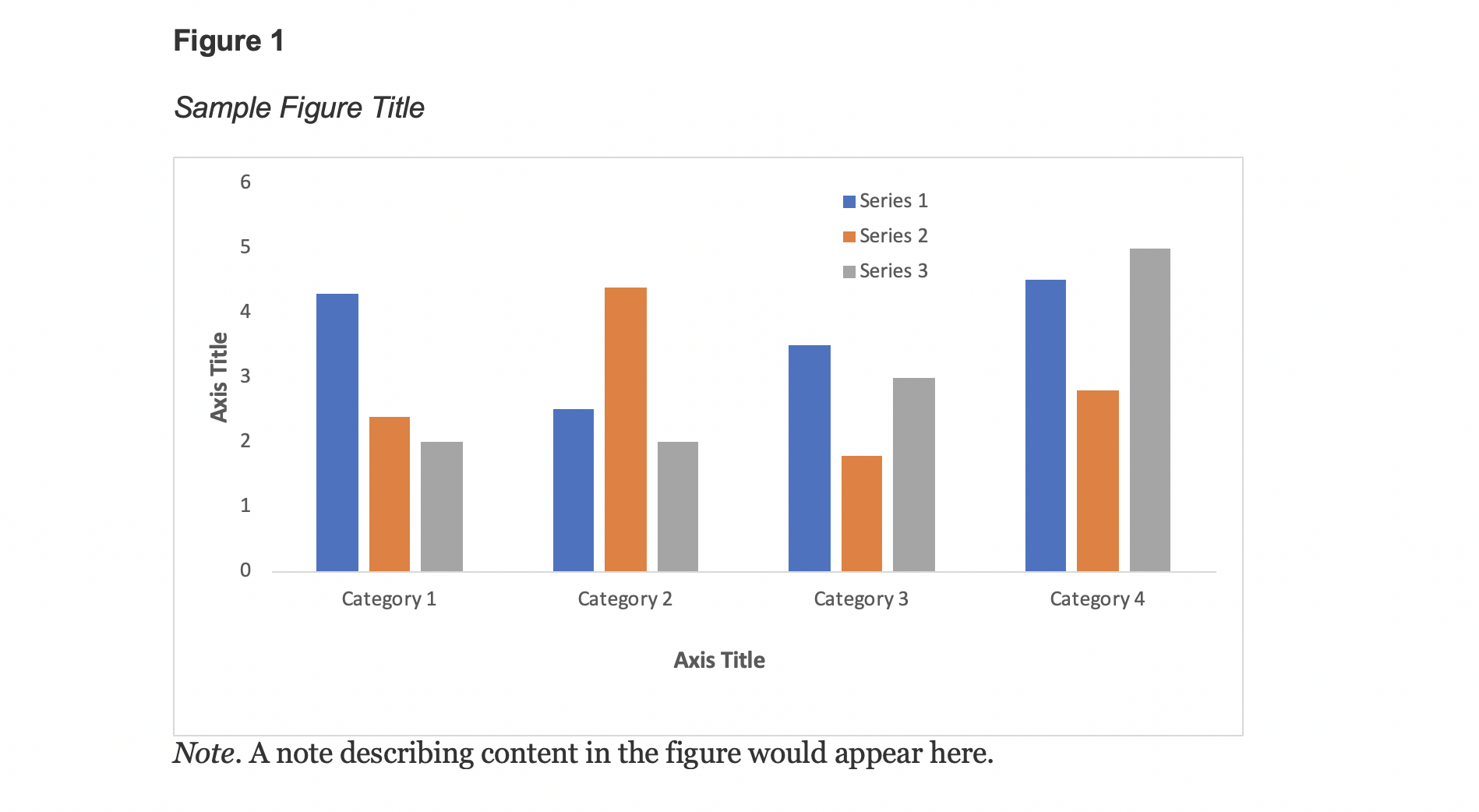
A generic example of a figure formatted in APA 7 style.
(Taken from the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association, 7th ed., Section 7.35)
Source:
Purdue Online Writing Lab. (n.d.). APA Tables and Figures. Purdue Online Writing Lab. https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/apa_style/apa_formatting_and_style_guide/apa_tables_and_figures.html
